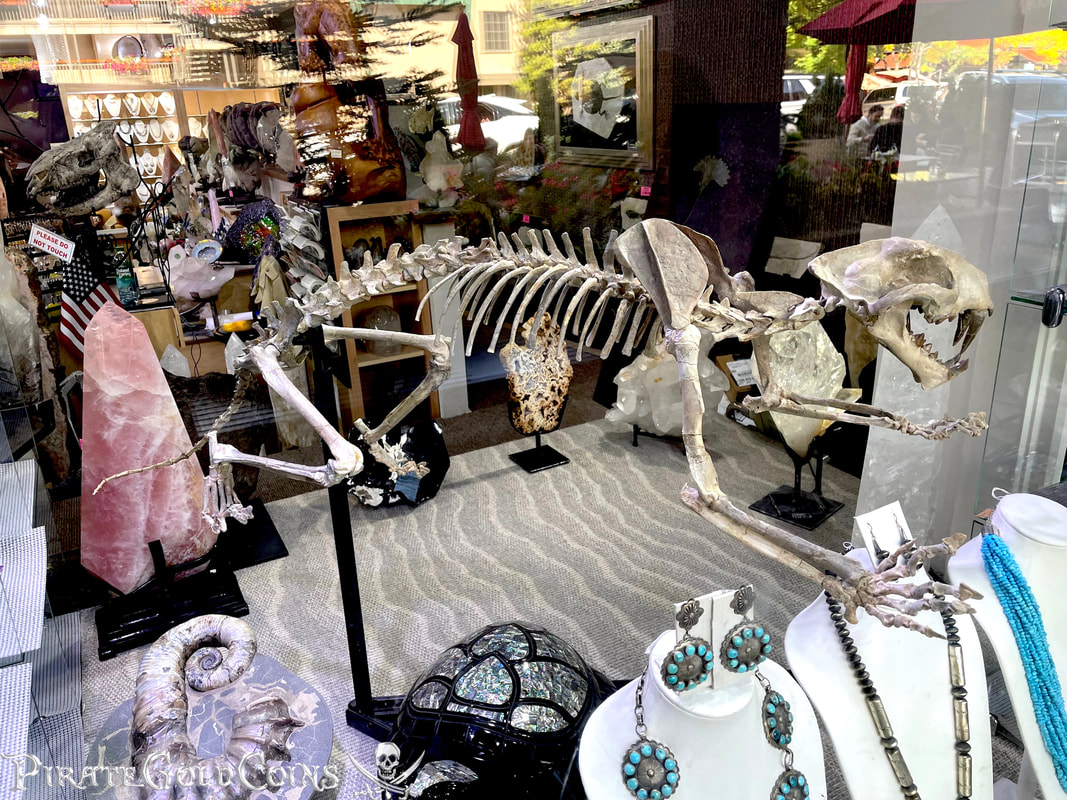
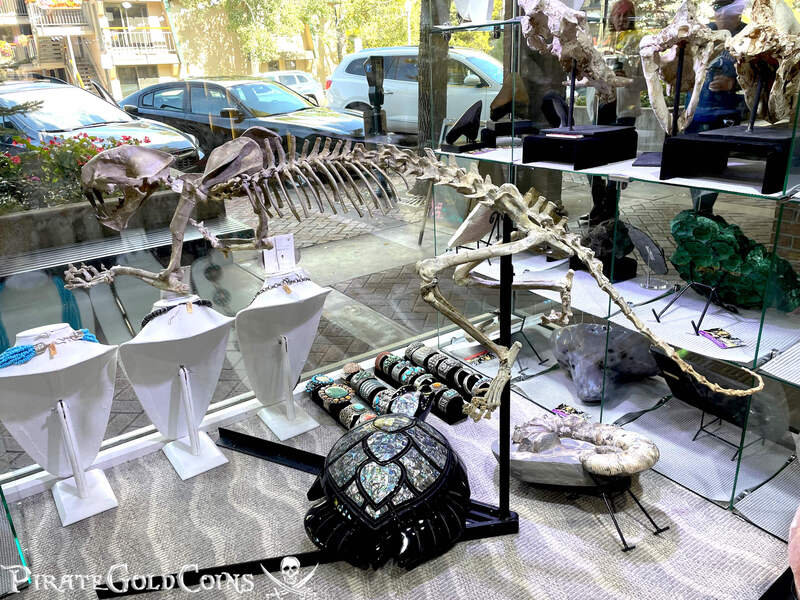
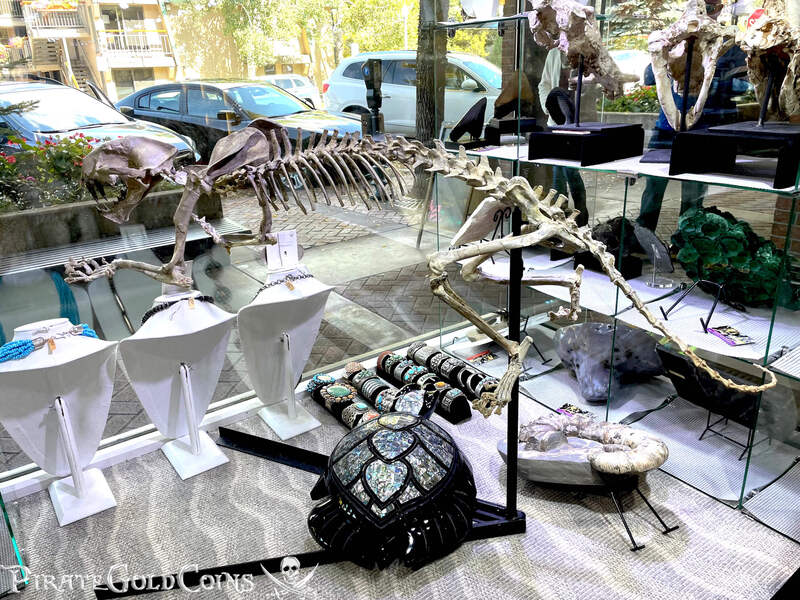
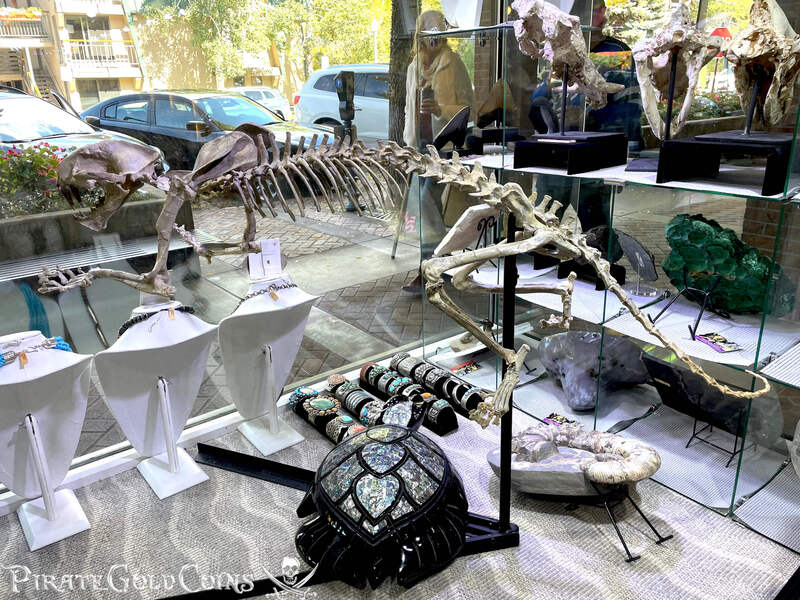
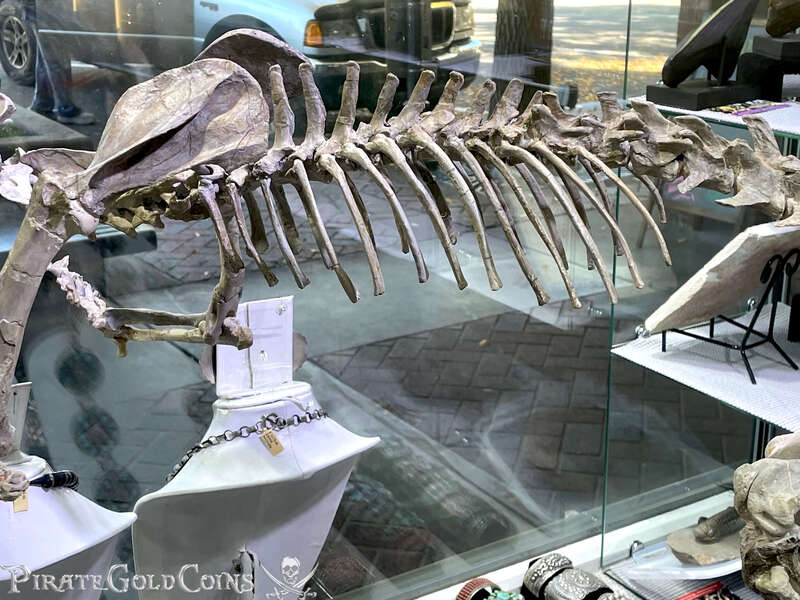
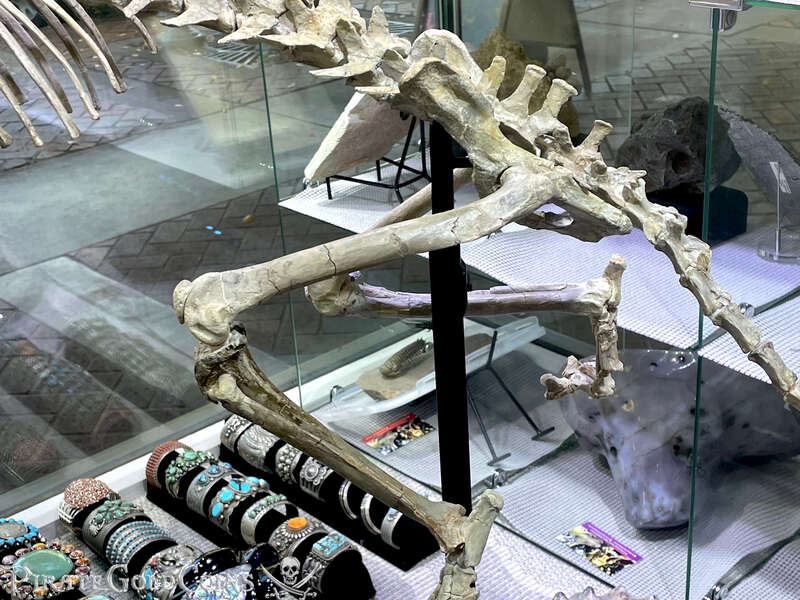
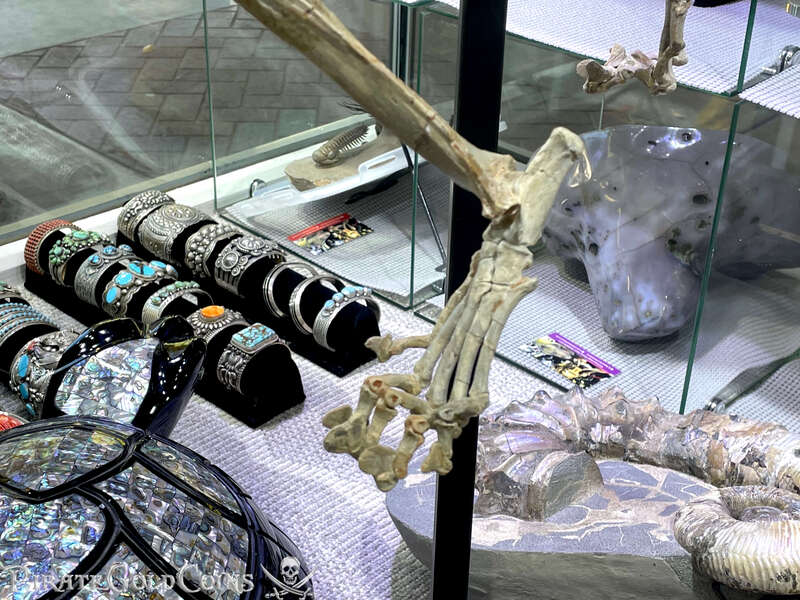
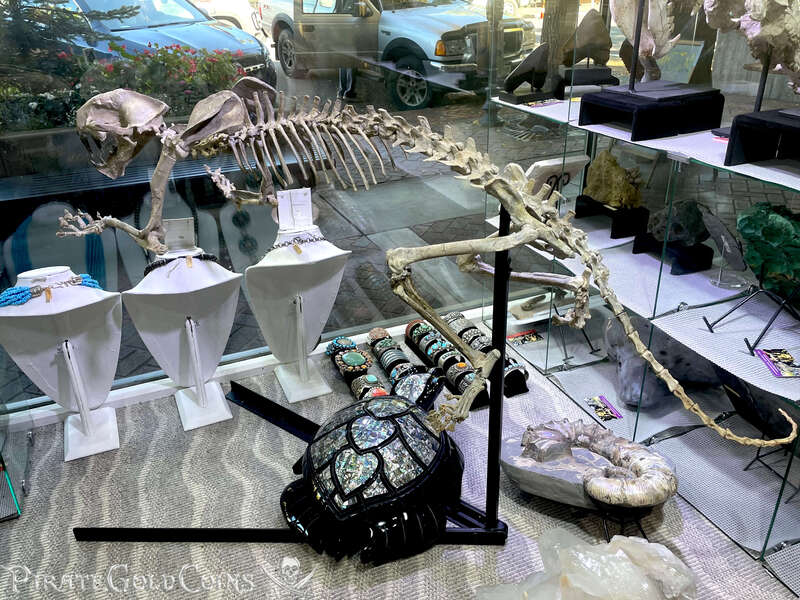
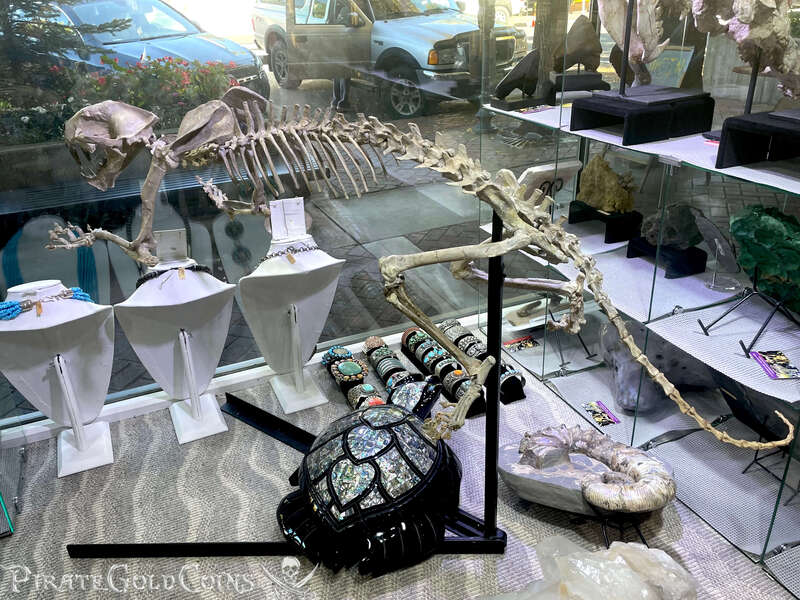
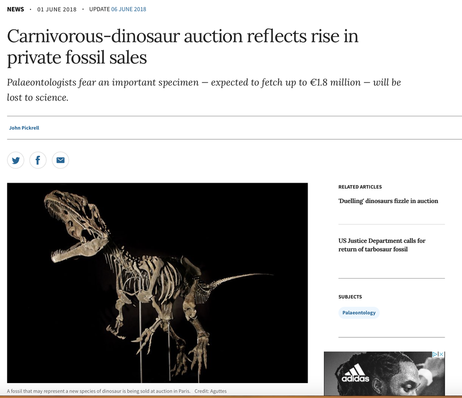
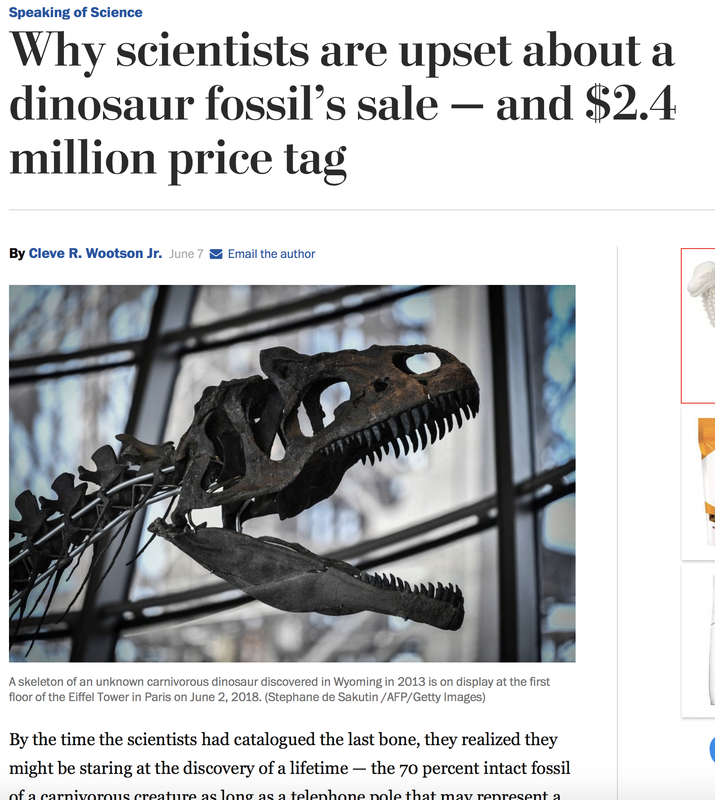
Pirate Gold Coins: Treasures of the Jurassic - Baby Saber Tooth Tiger
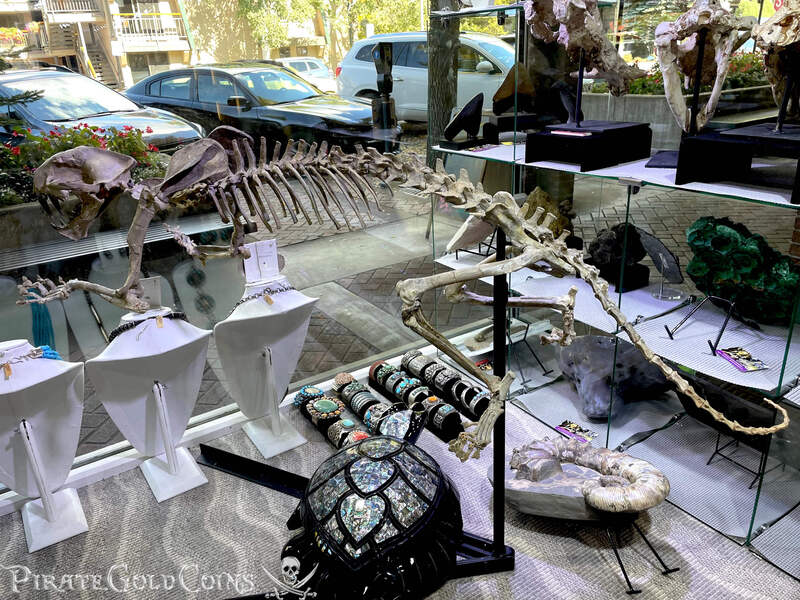
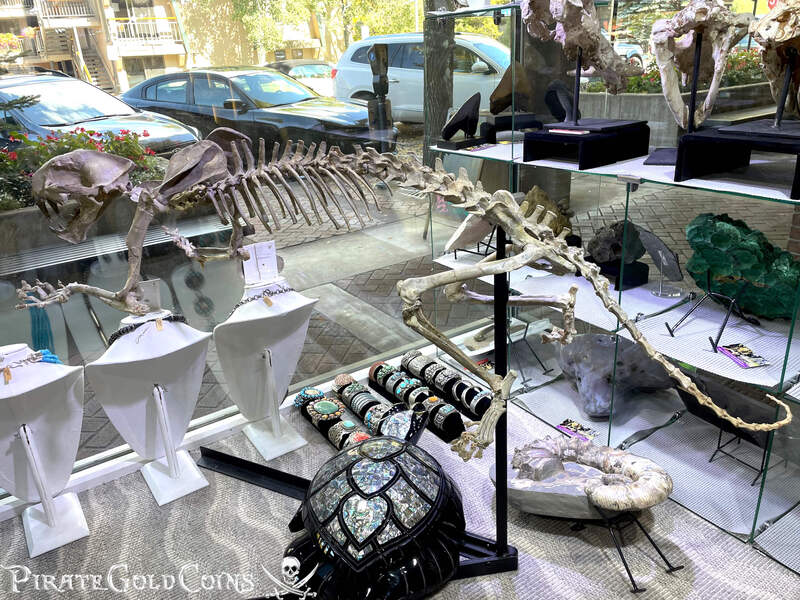
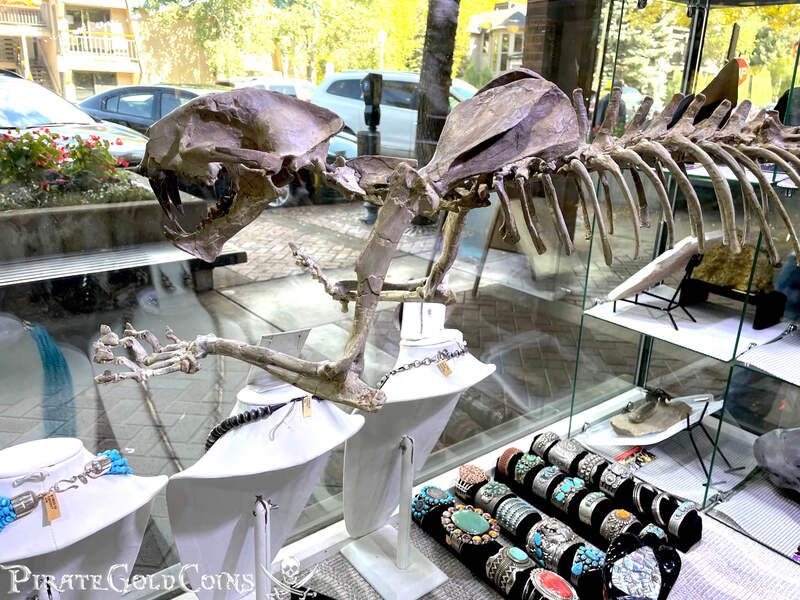
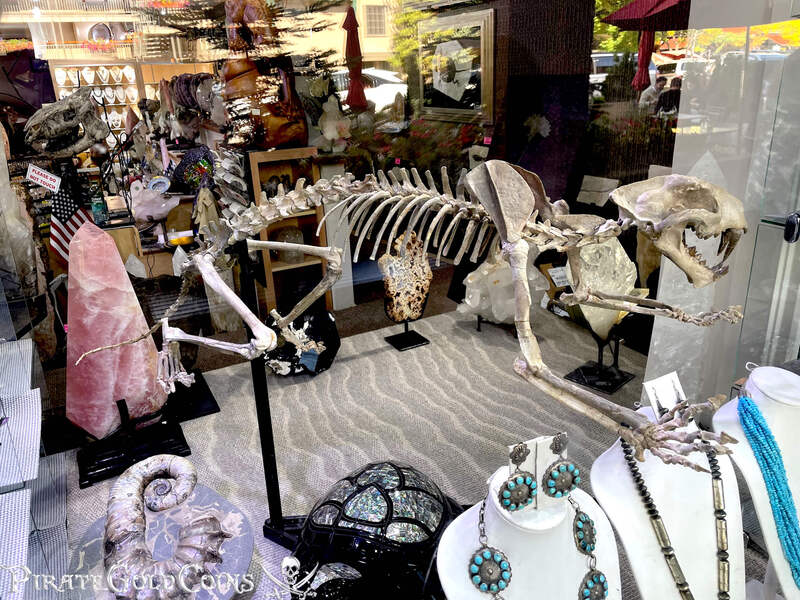
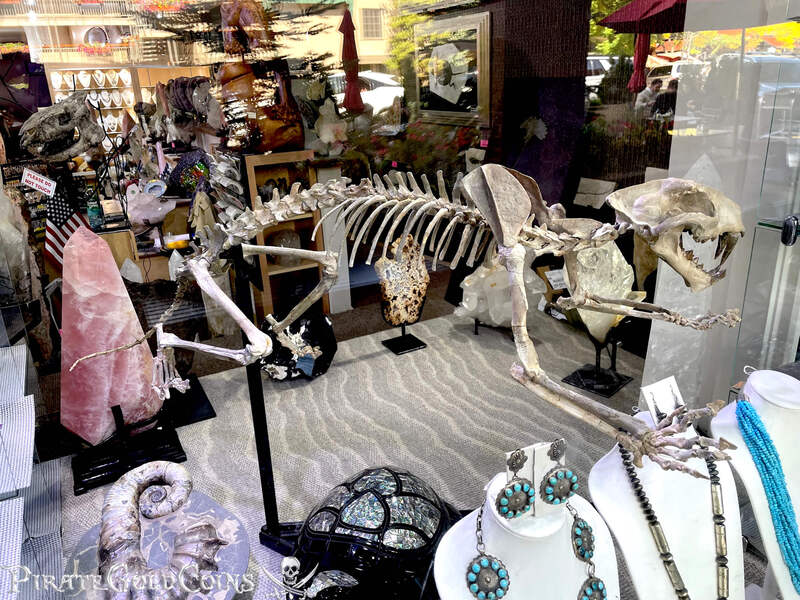
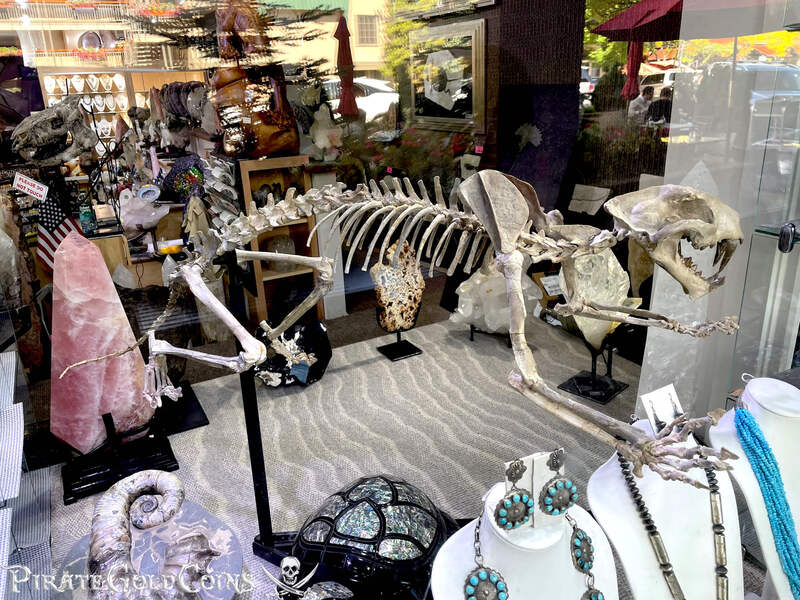
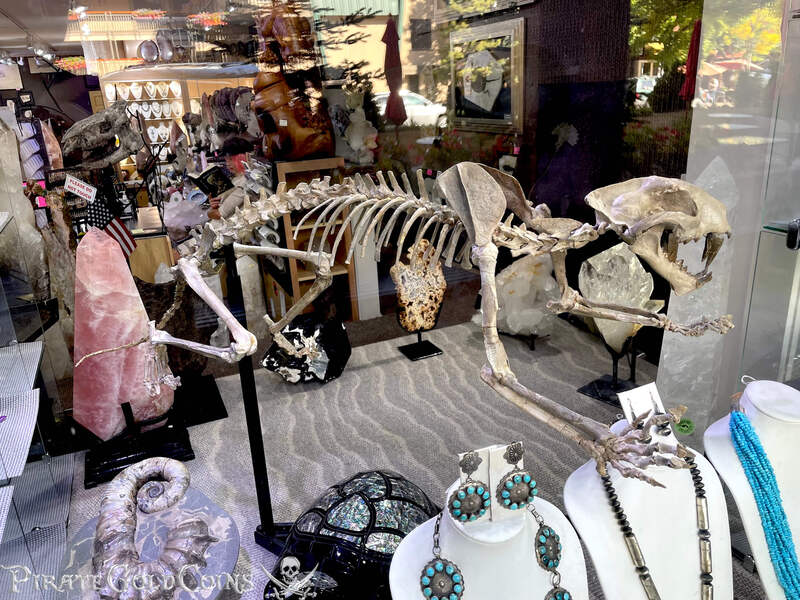
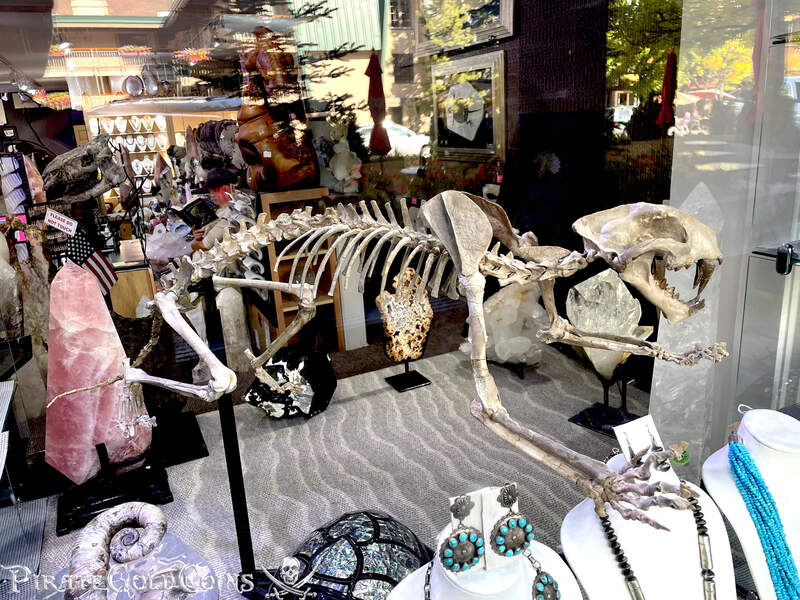
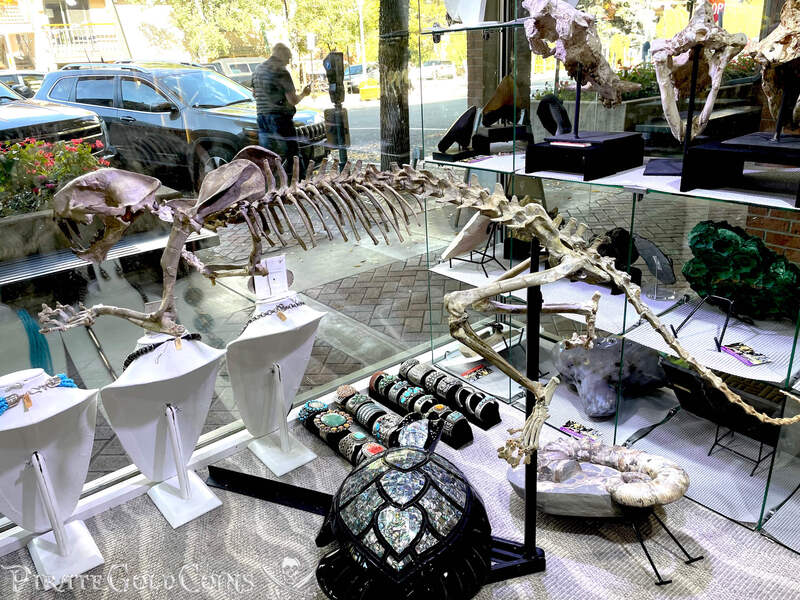
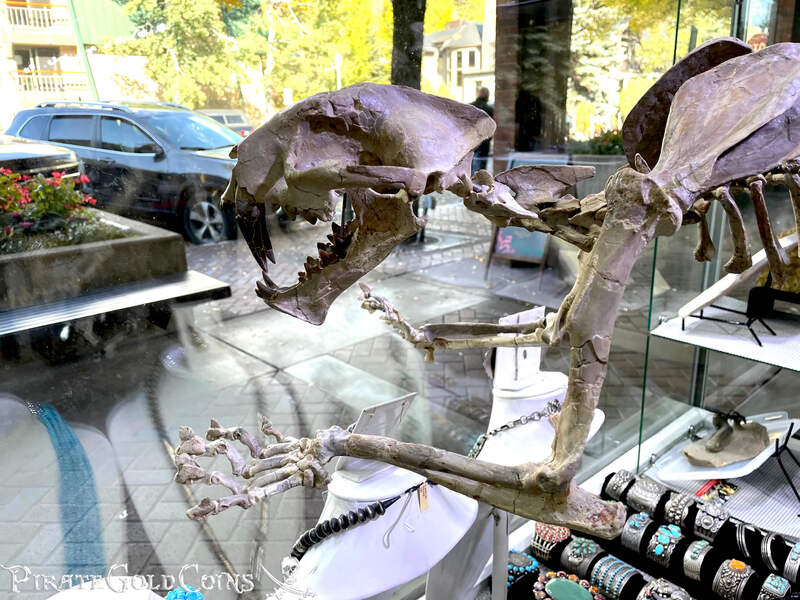
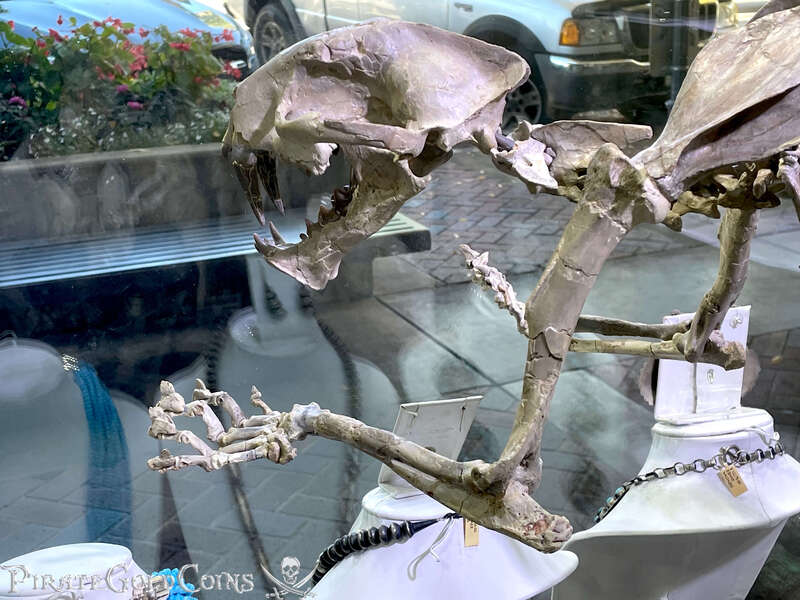
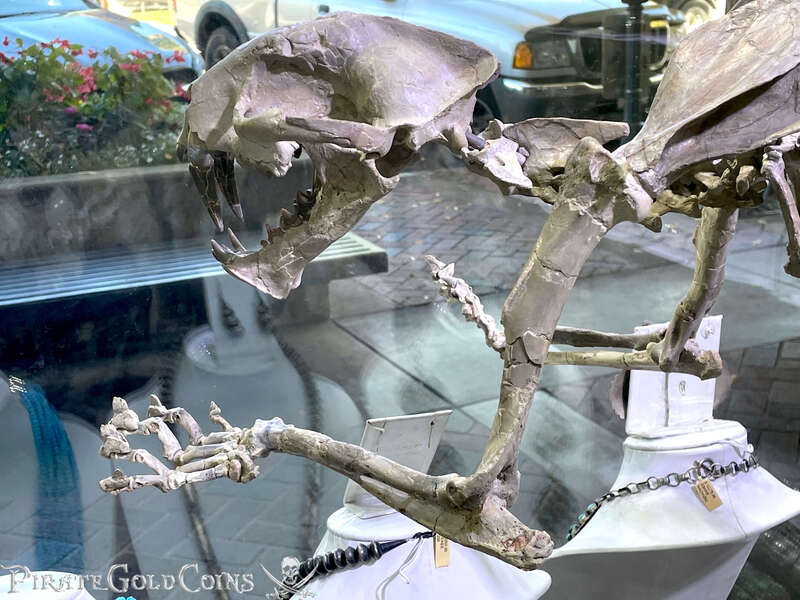
A saber-toothed cat (alternatively spelled sabre-toothed cat) is any member of various extinct groups of predatory mammals and non-mammalian therapsids that are characterized by long, curved saber-shaped canine teeth which protruded from the mouth when closed. The saber-toothed cats have been found almost worldwide from the Eocene epoch to the end of the Pleistocene epoch 42 million years ago (mya) – 11,000 years ago (kya).
One of the best-known genera is Smilodon, the species of which, especially S. fatalis, are popularly, but incorrectly, referred to as "saber-toothed tigers". However, usage of the word cat is in some cases a misnomer, as many species referred to as saber-toothed "cats" are not closely related to modern cats (Felidae). Instead, many members are classified into different families of Feliformia, such as Barbourofelidae and Nimravidae; the oxyaenid "creodont" genera Machaeroides and Apataelurus; and two extinct lineages of metatherian mammals, the thylacosmilids of Sparassodonta, and deltatheroideans, which are more closely related to marsupials. In this regard, these saber-toothed mammals can be viewed as examples of convergent evolution. This convergence is remarkable due not only to the development of elongated canines, but also a suite of other characteristics, such as a wide gape and bulky forelimbs, which is so consistent that it has been termed the "saber-tooth suite."
Of the feliform lineages, the family Nimravidae is the oldest, entering the landscape around 42 mya and becoming extinct by 7.2 mya. Barbourofelidae entered around 16.9 mya and were extinct by 9 mya. These two would have shared some habitats.
The different groups of saber-toothed cats evolved their saber-toothed characteristics entirely independently. They are most known for having maxillary canines which extended down from the mouth when the mouth was closed. Saber-toothed cats were generally more robust than today's cats and were quite bear-like in build. They are believed to have been excellent hunters, taking animals such as sloths, mammoths, and other large prey. Evidence from the numbers found at the La Brea Tar Pits suggests that Smilodon, like modern lions, was a social carnivore.
The first saber-tooths to appear were non-mammalian synapsids, such as the gorgonopsids; they were one of the first groups of animals within Synapsida to experience the specialization of saber teeth, and many had long canines. Some had two pairs of upper canines with two jutting down from each side, but most had one pair of upper extreme canines. Because of their primitiveness, they are extremely easy to tell from machairodonts. Several defining characteristics are a lack of a coronoid process, many sharp "premolars" more akin to pegs than scissors, and very long skulls.
One of the best-known genera is Smilodon, the species of which, especially S. fatalis, are popularly, but incorrectly, referred to as "saber-toothed tigers". However, usage of the word cat is in some cases a misnomer, as many species referred to as saber-toothed "cats" are not closely related to modern cats (Felidae). Instead, many members are classified into different families of Feliformia, such as Barbourofelidae and Nimravidae; the oxyaenid "creodont" genera Machaeroides and Apataelurus; and two extinct lineages of metatherian mammals, the thylacosmilids of Sparassodonta, and deltatheroideans, which are more closely related to marsupials. In this regard, these saber-toothed mammals can be viewed as examples of convergent evolution. This convergence is remarkable due not only to the development of elongated canines, but also a suite of other characteristics, such as a wide gape and bulky forelimbs, which is so consistent that it has been termed the "saber-tooth suite."
Of the feliform lineages, the family Nimravidae is the oldest, entering the landscape around 42 mya and becoming extinct by 7.2 mya. Barbourofelidae entered around 16.9 mya and were extinct by 9 mya. These two would have shared some habitats.
The different groups of saber-toothed cats evolved their saber-toothed characteristics entirely independently. They are most known for having maxillary canines which extended down from the mouth when the mouth was closed. Saber-toothed cats were generally more robust than today's cats and were quite bear-like in build. They are believed to have been excellent hunters, taking animals such as sloths, mammoths, and other large prey. Evidence from the numbers found at the La Brea Tar Pits suggests that Smilodon, like modern lions, was a social carnivore.
The first saber-tooths to appear were non-mammalian synapsids, such as the gorgonopsids; they were one of the first groups of animals within Synapsida to experience the specialization of saber teeth, and many had long canines. Some had two pairs of upper canines with two jutting down from each side, but most had one pair of upper extreme canines. Because of their primitiveness, they are extremely easy to tell from machairodonts. Several defining characteristics are a lack of a coronoid process, many sharp "premolars" more akin to pegs than scissors, and very long skulls.